Welcome to our guide on “Blocking Risks Indexing”! Have you ever wondered why some parts of your website might not show up in Google or other search engines? It’s all about whether search engines can see and understand your content. If they can’t, then people searching online won’t be able to find those parts of your site. This guide is here to help you figure out why this happens and what you can do about it.
We’re going to explore what these obstacles might be, from little mistakes in a file called robots.txt to bigger issues like server downtime. Then, we’ll give you some handy tips on how to fix these issues, so your website can be easily found and enjoyed by everyone.
Understanding Blocking Risks Indexing
When you create a website, you want people to find it easily, right? For that to happen, search engines like Google need to be able to look through your site and show it in search results. This process is called “indexing.” However, sometimes there are hurdles that can stop search engines from seeing parts of your website. This is what we mean by “blocking risks indexing.”
What Does Blocking Risks Indexing Mean?
Imagine you have a store with some doors closed; search engines are like visitors who can only see what’s inside the open doors. If important doors are closed, they miss seeing what’s inside those rooms. Similarly, if parts of your website are blocked, search engines won’t see them and won’t show these parts in search results. This means fewer people can find your website.
Why Does Blocking Happen?
Blocking can happen for a few reasons, and here are some of the main ones:
- Robots.txt File Issues: This is a small file that tells search engines which parts of your site they can or cannot check out. If it’s set up wrong, it might tell search engines not to look at important parts of your site.

- Meta Tags and Headers: These are like signs on your pages that give search engines special instructions. For example, a ‘noindex’ tag tells search engines not to show that page in search results. If these signs are put up by mistake, you might be hiding parts of your site without meaning to.
- Errors in Links to Pages (Canonical Tags): Sometimes, websites have similar or duplicate content and use special links (canonical tags) to tell search engines which version is the main one. If these links are wrong, search engines might get confused and ignore important pages.
- Server Problems: If your website’s server is often down or has errors, search engines might have a hard time visiting your site to index it.
- Complicated Designs (JavaScript or AJAX): Websites that use a lot of fancy code might look great but can be hard for search engines to read. If search engines can’t understand your site’s content, they might not index it properly.
How Can You Fix These Issues?
- Check Your Robots.txt: Make sure it’s not accidentally blocking important parts of your site.
- Use Meta Tags Wisely: Only use ‘noindex’ tags on pages you really don’t want to show up in search results.
- Fix Your Canonical Tags: Make sure they point to the correct pages.
- Keep Your Server Healthy: Make sure your website is always available and quick to load.
- Simplify Your Site’s Code: If your site uses a lot of JavaScript or AJAX, make sure it’s set up in a way that search engines can still read your content.
What’s Next?
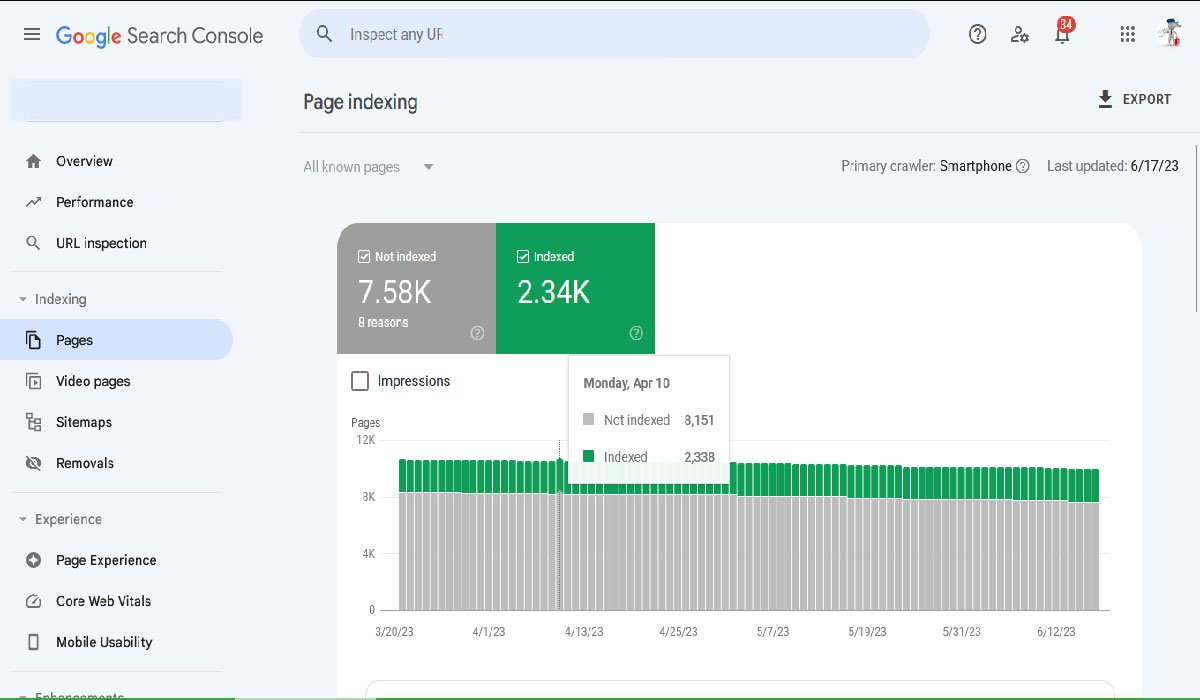
It’s a good idea to regularly check how your website is doing in tools like Google Search Console. This tool can tell you what parts of your site are indexed and if there are any problems. By keeping an eye on these things, you can make sure your website is easy for search engines to read and for people to find.
Tools and Techniques for Identifying Indexing Issues
- Google Search Console: This free tool from Google allows you to see exactly how Google views your site, what’s indexed, and what’s not, along with the specific reasons for non-indexation.
- Site Audit Tools: Software like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, and SEMrush can simulate how search engines crawl your site and spot potential indexing issues like broken links or server errors.
- Manual Checks: Periodically reviewing your site’s robots.txt file, meta tags, and canonical links manually can save you from unexpected indexing issues.
Mitigation Strategies to Enhance Indexing
- Optimize Your Robots.txt: Regularly update and optimize your robots.txt file to ensure it accurately reflects the sections of your site you want to be crawled and indexed.
- Correct Use of Meta Tags and Headers: Utilize meta tags and HTTP headers correctly by ensuring that ‘noindex’ directives are only applied where absolutely necessary.
- Proper Canonical Tags: Verify that all canonical tags point to the correct URLs and rectify any mismatches or incorrect implementations.
- Improve Server Response: Monitor your server’s performance and optimize it to avoid downtime and slow response times, which can impact search engine access and indexing.
- Adapt Content for Better Crawling: If using a lot of JavaScript or AJAX, consider server-side rendering or other techniques to make sure search engines can see and index your content effectively.
Conclusion
Blocking risks indexing can significantly impede your SEO efforts by hiding your content from search engine view. By understanding the common causes and employing targeted mitigation strategies, you can ensure that your site remains accessible and attractive to search engines. Regular monitoring, updating your SEO practices, and conducting thorough site audits are crucial to maintaining an optimal indexing status and achieving long-term success in the digital landscape.
FAQs About Blocking Risks Indexing
What is blocking risks indexing?
Blocking risks indexing refers to issues that prevent search engines from accessing and indexing parts of your website. If search engines can’t see your content, it won’t appear in search results, which can reduce your site’s visibility and traffic.
How do I know if my website has blocking risks indexing?
You can use tools like Google Search Console to check for indexing issues. This tool shows whether all pages are being indexed and highlights any pages that are blocked. Also, regularly checking your robots.txt file and meta tags can help identify any potential blocks.
What is a robots.txt file and how does it affect indexing?
A robots.txt file is a text file that tells search engines which parts of your website they can or cannot access. Misconfigurations in this file can accidentally block important parts of your site from being indexed.
Read Also: Kimbsxo: Revolutionizing Fashion with Authenticity and Innovation
For More Information Visit Walker Magazine
















Leave a Reply